Fiber Optic Cabling
GETTING YOUR BUSINESS CONNECTED, FAST!
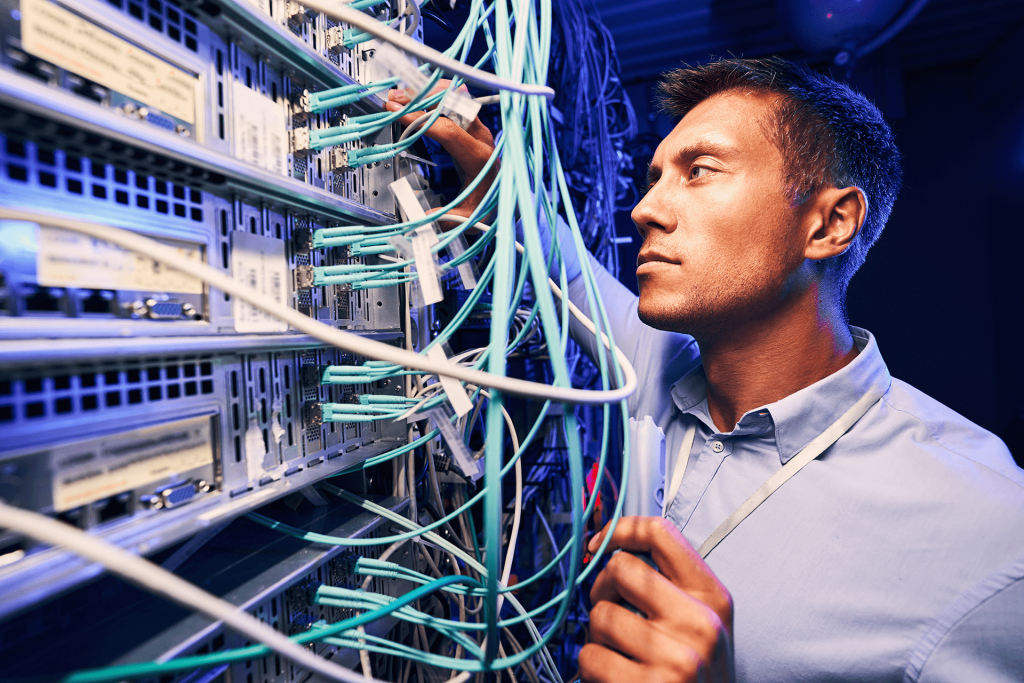
FIBER OPTIC CABLING INSTALLATION
While high-end copper networks can transmit low gigabit speeds, they have a number of flaws, including signal degradation, interference, inefficiency, and asymmetrical speeds (i.e. where download speeds are much higher than upload speeds). Fiber optic cables can transmit data at up to 100 gigabits per second with low power requirements, symmetrical speeds, no electrical interference, and are corrosion resistant.
What Is Fiber Optic Cable?
Fiber optic cabling is a superior option in nearly all applications, just as long as it isn’t prohibitive to install the proper infrastructure.
There are two types of cable used to transmit signals in data networks like the internet: copper wire and fiber optics. Copper is by far the oldest type of cable in use — ethernet cables are an example of low-voltage signal transmission cabling, and coaxial cable is another common type. Low-voltage pulses of electricity pass through copper wire and are converted into binary data that is processed by a computer at the other end. The information in fiber optic wire travels down a glass filament in the form of light pulses, which the computer processes.